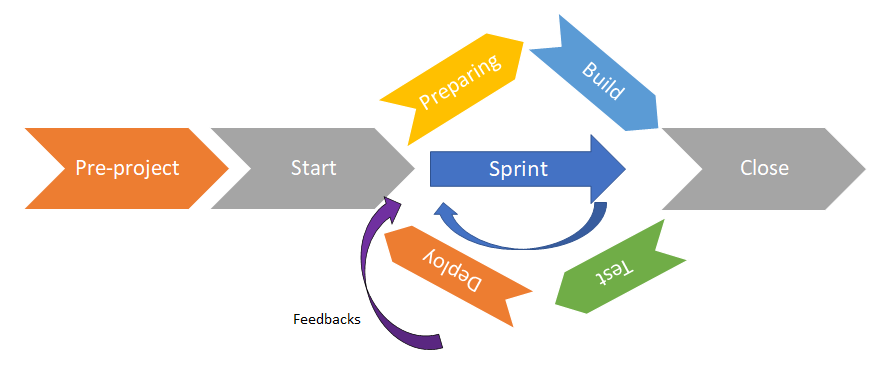
Agile's principles
Reminder on the principles of agile:- Focusing on value
- Respecting for people
- Minimizing the waste
- Being transparent
- Adapting to change
- Continuously improving

| Responsible | Accountable | Consulted | Informed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Owner | Product Owner | Users | Project Team |
| Version | Date | Author | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 2021/01/06 | Emeline Robert Aubrun @manageprojects.tech | Initialization |
| Document | Version | Link | Description |
|---|
It is deployed on production environments BUT is not not used or used by a small part of the users (this is called the pilot phase).
It is accessible and used by all users.
Document allowing all parties to trace the delivery of deliverables.
Decision of all parties to proceed to the next step.
GO's decision can be qualified: prior actions must then be taken
(e.g. corrections or rapid corrective delivery planning).
Comes after the crash of servers, databases, etc., it is a function of uploading the application from the backups.
System adopted to guarantee the expected service rate.
Describes who does what on the project. The different responsibilities :
Responsible / Accountable / Consulted / Informed.