The life cycle of an IS project
The 7 phases of a project
Depending on the type of project, the phases will not be the same.For the moment, whatever the chosen methodology, a project is divided into 7 phases :
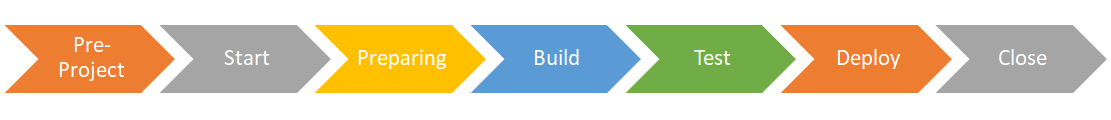
- Pre-Project/Initiate: define the project opportunities with the scope and expected benefits.
- Start/Define: study the solutions and describe the expected progress of the project.
- Preparing/Design: define the functional and operational business needs, the functional and application architecture, the solution design and the cost estimation.
- Build: build the application, determine test scenarios and change management
- Test: validate how the solution works according to the documentation and study possibility of production deployment.
- Deploy: deploy the solution on production, implemente the change management, switch from project mode to RUN mode.
- Close: check the documentation and assess the application (stability and expected result). Note that following this phase, we are no longer talking about a project but about an application that enters the RUN phase with maintenance corrective (only concerns bug correction) and evolutionary maintenance.
The first 2 phases (pre-project and start) are the preliminary project phases, the next 4 ones are the specific project phases (preparing, build, test, deploy) and the last one marks the end of the project.
At the beginning of the pre-project phase, the business must have produced a project sheet and have estimated the ROI (Return on Investment) of the project.

During the Define phase, the project methodology will be defined.
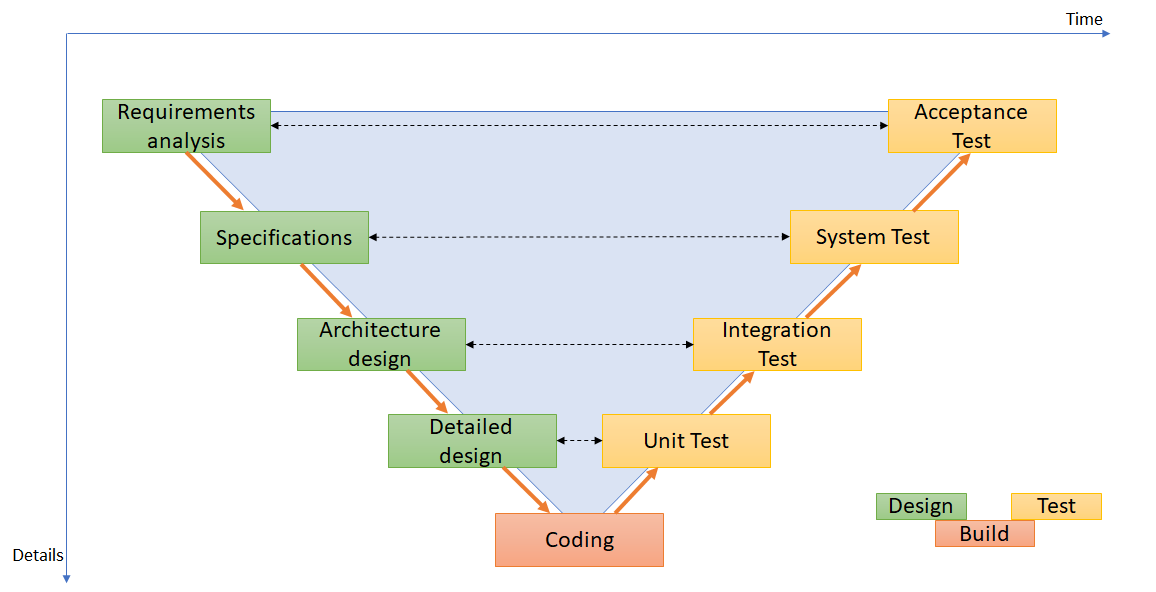
Project with Waterfall method (Verification and Validation Model)
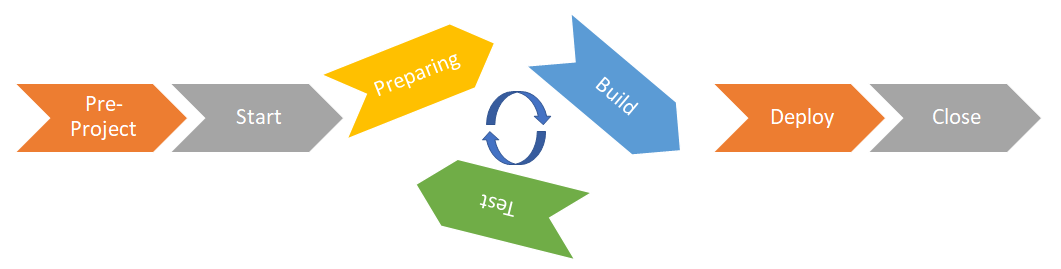
Iterative project
In some projects where I have been involved, the notion of iterative has been integrated into the V projects.The start phase is a classic one : the macro scope / planning / budget are defined. Then the general design is carried out to locate the different functional blocks (and their dependencies) in the applications and identify the maturity of the requirement. Then the need is subdivided (with the possibility of remaining flexible on the addition/modification of functions according to the perimeter modification process defined in the project charter) and the detailed preparing, build and test phases follow one another for each batch until the end of the batches and the deployment of the entire application.
RAD (Rapid Application Development)
It shrinks the process into 5 phases :
- Pre-project/Initiate: definition of the scope, project themes and resources required.
- Start/Define: expression of needs during workshops with working groups.
- Preparing/Design: design with system modeling. Users can be included to validate the models, ergonomics and general kinematics of the application.
- Build: the team builds the solution iteratively, by module or by theme with user validation.
- Close: Formalize the global delivery of the application already partially validated by users
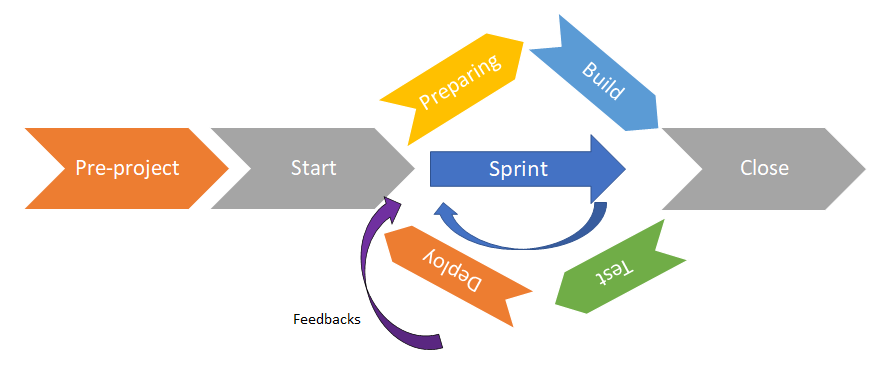
Agile project
In the pre-project phase, an overall goal must be defined and shared between all stakeholders to have an idea of the way to follow.The Agile methodology is an empirical methodology: it allows you to set short-term objectives. Once this last one is achieved, a new short-term objective will be decided.
Then, depending on the challenge (for example :limited budget or deadline for regulations, for example), short-term objectives will be prioritized.
The functions which bring the most value to users (and are the most risky) must be prioritized.
Objectives and output
| Phase | 1.Initiate Pre-project | 2.Define Start | 3.Design Preparing | 4.Build | 5.Test | 6.Deploy | 7.Close |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objectives | * Study the opportunities of the project. * Clarifying the business need. |
* Define the solution. * Define the organization and costs of the project. |
* Design the solution (general and detailed). | * Build the solution * Prepare for deployment. |
* Test applications. | * Deploy applications. * Switch from project mode to RUN mode. |
* Check the documentation. * Confirm the stability and the functions of the solution. |
| Deliverables | * Business Case * Security analysis. |
* Detailed description of the business need * Related business objects * The needs of the connected IS (back-end and middleware) * Specifications of the project * GO next phase. |
* Design documentation * Data model * Strategy for deployment, migration and for acceptance, load and performance testing * Security analysis * Interface contracts * GO next phase. |
* Technical and operating specifications * Requirements for production launch, commissioning and RUN * Deployment plan * Test Scenario * Recovery plan/ Service continuity plan * Solution delivery report * Documentation delivery report * GO next phase. |
* Functional test report * Interface, load and performance testing report * GO next phase. |
* Production Requirements+GO *Anomalies resolution plan * Requirements for commissioning * Requirements for RUN+GO. | * Project review (Business and IT). |